In this document
Introduction
The easiest way of starting a new project using ABP with ASP.NET Core MVC is to create a template on the download page. After creating and downloading your project, follow the steps below to run your application.
-
Open your solution in Visual Studio 2019 (v16.4)+ and build the solution.
-
Select the 'Web.Mvc' project as the startup project.
-
Check the connection string in the appsettings.json file of the Web.Mvc project, change it if you want.
-
Open Package Manager Console and run the Update-Database command to create your database (ensure that the Default project is selected as .EntityFrameworkCore in the Package Manager Console window).
-
To download and build the project’s client-side packages, we use gulp.
-
For development:
Open a terminal in the Web.Mvc folder and run:npm run create-bundles -
For production:
Open a terminal in the Web.Mvc folder and run:npm run build
These commands will download the required client-side packages and generate the necessary bundles for the application.
-
-
Run the application.
If you have problems with running the application, please try closing and opening Visual Studio again. It sometimes fails on first package restore.
Login
Once you run the application, you will see the following login page:
The username is 'admin' and the password is '123qwe' by default. There is also a "Default" tenant. After you login, you can see the sample dashboard page:
About Multi-Tenancy
In this template, multi-tenancy is enabled by default. You can disable it in Core project's module class if you don't need it.
Token Based Authentication
The startup template uses cookie-based authentication for browsers. However, if you want to consume Web APIs or application services (those that are exposed via the dynamic web api) from a mobile application, you'll probably want a token-based authentication mechanism. The startup template includes JwtBearer token authentication infrastructure.
Here, Postman (Chrome extension) will be used to demonstrate requests and responses.
Authentication
Just send a POST request to http://localhost:62114/api/TokenAuth/Authenticate with a Content-Type="application/json" header as shown below:

We sent the values usernameOrEmailAddress and password. As seen above, the result property of the returning JSON contains the token and expiration time (which is 24 hours by default and can be configured). We can save it and use for the next requests.
**About Multi-Tenancy
**The API will work as host users by default. You can send a Abp.TenantId
header value to work with a specified tenant. It's an integer value and
1 for the default tenant by default.
Use API
After you authenticate and get the token, we can use it to call any authorized action. All application services can be used remotely. For example, we can use the User service to get a list of users:
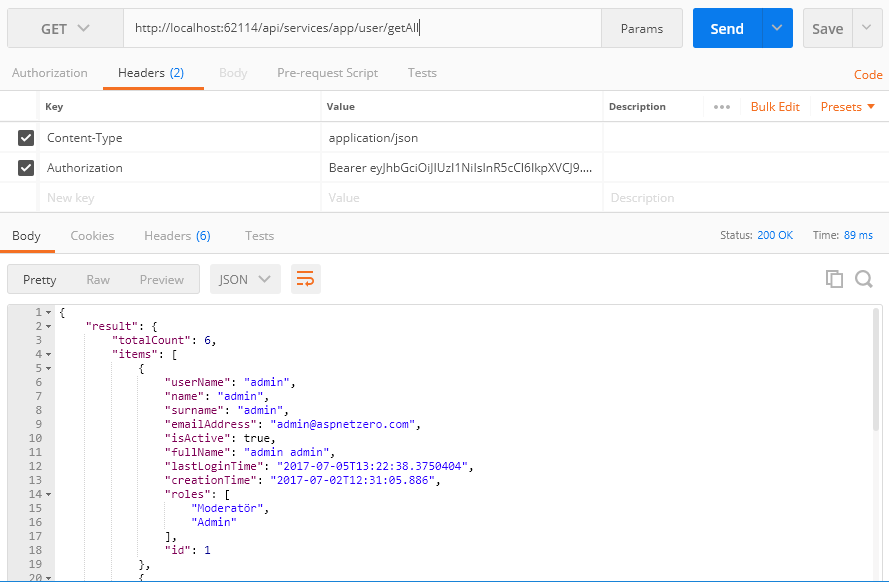
Just made a GET request to http://localhost:62114/api/services/app/user/GetAll with Content-Type="application/json" and Authorization="Bearer your- auth-token ".
Almost all operations available on the UI are also available as a Web API, since the UI uses the same Web API, and can be easily consumed.
Migrator Console Application
The startup template includes a tool, Migrator.exe, to easily migrate your databases. You can run this application to create/migrate the host and tenant databases.

This application gets the host connection string from it's own appsettings.json file. In the beginning, it will be the same in the appsettings.json in the .Web.Host project. Be sure that the connection string in the config file is the database you want. After getting the host connection string, it first creates the host database and applies migrations if they don't already exist. It then gets the connection strings of the tenant databases and runs migrations against those databases. It skips a tenant if it does not have a dedicated database or its database has already been migrated by another tenant (for shared databases between multiple tenants).
You can use this tool on the development or on the production environment to migrate databases on deployment instead of EntityFramework's own tooling (which requires some configuration and can only work for a single database/tenant in one run).
Unit Testing
The startup template includes the test infrastructure setup and a few tests under the .Test project. You can check them and write similar tests easily. They are actually integration tests rather than unit tests, since they test your code with all the ASP.NET Boilerplate infrastructure (including validation, authorization, unit of work...).
Running on Docker
The startup template includes necesary files for building docker images and running those images in docker.
Building Docker images
In order to build docker image, open the command prompt, go to aspnet-core/build folder and run build-mvc.ps1 script. This script will build abp/mvc docker image.
The default image is designed to use your local SQL Server, so don't foget to set ConnectionStrings__Default in aspnet-core/docker/mvc/docker-compose.yml before building the docker image. In order to connect your local SQL Server, you need to use your local IP address in the connection string.
A sample connection string is ConnectionStrings__Default: "Server=192.168.1.42; Database=AbpProjectNameDb; User=sa; Password=123qwe;TrustServerCertificate=True;"
Running the project
After creating the docker image, you can go to aspnet-core/docker/mvc folder and run up.ps1 script to run the docker image.
Source Code
This template is developed as an open source project and is available for free on GitHub: https://github.com/aspnetboilerplate/module-zero-core-template
