In this document
Introduction
This document is for the ASP.NET MVC and Web API. If you're interested in ASP.NET Core, see the ASP.NET Core documentation.
In a web application, exceptions are usually handled in MVC Controller and Web API Controller actions. When an exception occurs, the application user is informed about the error and with an optional reason.
If an error occurs in a regular HTTP request, an error page is shown. If an error occurs in an AJAX request, the server sends the error information to the client and the client then handles and shows it to the user.
Handling exceptions in all web requests is tedious, and hard to keep DRY. ASP.NET Boilerplate automates this. You almost never need to explicitly handle an exception. ASP.NET Boilerplate handles all exceptions, logs them, and returns an appropriate and formatted response to the client. It also handles these responses in the client and shows error messages to the user.
Enabling Error Handling
To enable error handling for ASP.NET MVC Controllers, customErrors mode must be enabled for ASP.NET MVC applications.
<customErrors mode="On" />
It can also be 'RemoteOnly' if you do not want to handle errors on a local computer, for instance. Note that this is only required for ASP.NET MVC Controllers, and not for Web API Controllers.
If you are already handling exceptions in a global filter, it may hide exceptions. Thus, ABP's exception handling may not work as you expected. So if you do this, do it carefully!
Non-Ajax Requests
If a request is not AJAX, an error page is shown.
Showing Exceptions
Imagine that there is an MVC controller action which throws an arbitrary exception:
public ActionResult Index()
{
throw new Exception("A sample exception message...");
}
Most likely, this exception would be thrown by another method that is called from this action. ASP.NET Boilerplate handles this exception, logs it and shows the 'Error.cshtml' view. You can customize this view to show the error. Here's an example error view (the default Error view in the ASP.NET Boilerplate templates):
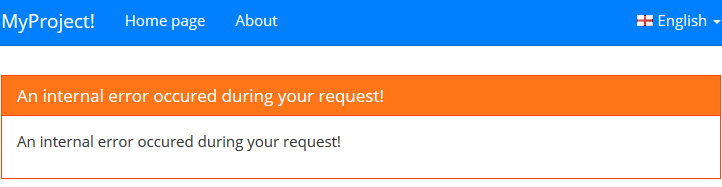
ASP.NET Boilerplate hides the details of the exception from users and shows a standard (and localizable) error message, unless you explicitly throw a UserFriendlyException.
UserFriendlyException
The UserFriendlyException is a special type of exception that is directly shown to the user. See the sample code below:
public ActionResult Index()
{
throw new UserFriendlyException("Ooppps! There is a problem!", "You are trying to see a product that is deleted...");
}
ASP.NET Boilerplate logs it and does not hide the exception:
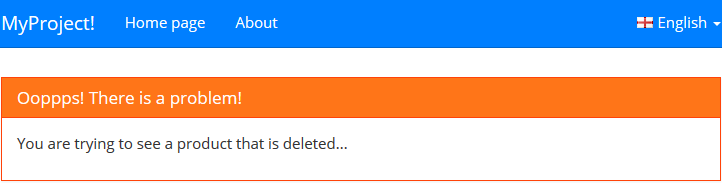
If you want to show a special error message to users, just throw a UserFriendlyException (or an exception derived from it).
Error Model
ASP.NET Boilerplate passes an ErrorViewModel object as a model to the Error view:
public class ErrorViewModel
{
public AbpErrorInfo ErrorInfo { get; set; }
public Exception Exception { get; set; }
}
ErrorInfo contains detailed information about the error that can be shown to the user. The Exception object is the thrown exception. You can check it and show additional information if you want. For example, we can show validation errors if it's an AbpValidationException:
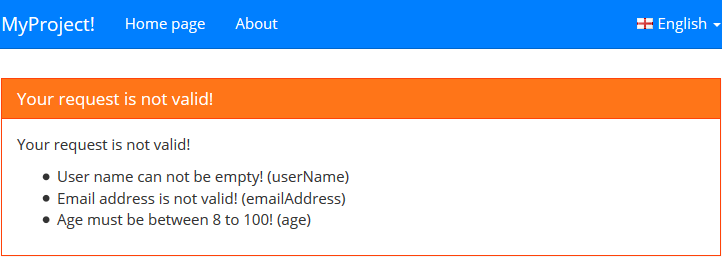
AJAX Requests
If the return type of an MVC action is a JsonResult (or Task<JsonResult for async actions), ASP.NET Boilerplate returns a JSON object to the client when exceptions occur. Sample return object for an error:
{
"targetUrl": null,
"result": null,
"success": false,
"error": {
"message": "An internal error occurred during your request!",
"details": "..."
},
"unAuthorizedRequest": false
}
success: false indicates that there is an error. The error object provides the message and details.
When you use ASP.NET Boilerplate's infrastructure to make an AJAX request on the client side, it automatically handles this JSON object and shows an error message to the user using the message API. See the AJAX API documentation for more information.
Exception Event
When ASP.NET Boilerplare handles an exception, it triggers an AbpHandledExceptionData event. (See eventbus documentation for more information about Event Bus). Example:
public class MyExceptionHandler : IEventHandler<AbpHandledExceptionData>, ITransientDependency
{
public void HandleEvent(AbpHandledExceptionData eventData)
{
//TODO: Check eventData.Exception!
}
}
If you put this example class into your application (generally into your Web project), the HandleEvent method will be called for all exceptions handled by ASP.NET Boilerplate. From there, you can investigate the Exception object in detail.
